Previous Next
Indian Geography (Part-10)
Peninsular Indian Plateau
Peninsula: - The part of the continent that is surrounded by oceans on three sides, such an area of the terrain is called a peninsula. Peninsular India is surrounded on the east by the Bay of Bengal, on the south by the Indian Ocean and the west by the Arabian Sea.we call it the plateau of peninsular India. Peninsular India does not have a high peak like a mountain, but there is a flat raised part of the rocks here.
The plateau of peninsular India is part of Gondwanaland. The plateau of peninsular India broke from Africa and flowed towards the north-east, due to its flow in the north-east pressure started to act on the debris in the Tethys Sea that resulted in the formation of curved hills of the Himalayas. Peninsular India is still flowing north-east, due to which the height of the Himalayas is still increasing.
The plateau of peninsular India is tectonically stable, due to which earthquakes do not normally occur in peninsular India. The movement inside the earth is called tectonics.
- The Aravali hills are situated on the north-western side of peninsular India, the Rajmahal hills are situated on its north-eastern side.
- Peninsular plateau of India spans from Aravali hills in west, Rajmahal hills in east and Kanyakumari in the south.
- The Shillong plateau in Meghalaya is also the northeastern extension of the plateau of peninsular India. The Shillong plateau is an extension of Rajmahal hills towards east.
- The slope of the northern part of the plateau of peninsular India is towards the north, that is, towards the Ganges valley, this is the reason that the Chambal, Betwaand Son rivers flow north-east and join the Ganges and Yamuna rivers.
Note -
- Chambal and Betwa river merges in Yamuna river near Etawah.
- Son river merges in Ganges river near Patna.
- Yamuna river merges the Ganges river in Allahabad (Prayagraj).
- To the south of the Satpura hill, the plateau of peninsular India slopes towards the east, that is why the rivers Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri ends in the Bay of Bengal flowing towards the east.
- To the north of the Satpura hill is the rift valley of the Narmada river and to the south is the rift valley of the Tapi river.
- Two rift valleys lie on the western side of the plateau of peninsular India, one of the rift valleys is north of Satpura and the other is south of Satpura.
Note - The concave area is called a rift valley.
- Narmada river flows in the northern rift of Satpura, hence it is called Narmada rift valley.
- The Tapi / Tapti River flows south of Satpura, hence it is called Tapi/Tapti Rift Valley.
- The slope of the Narmada and Tapi rift valleys is towards the west that is why the rivers the Narmada and Tapi flow in the west direction unlike the normal slope of peninsular India.
- The rivers Narmada and Tapi end in Gulf of Khambhat. the Arabian Sea.
- The Western Ghat Mountains extend from the mouth of the Tapi River to the West Coast as well as the Cardamom Hills in Kerala, while the Eastern Ghat Mountains extend along the East Coast.
- The mountain ranges of the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats merge in South India, due to which a mountain knot is formed, this mountain knot is called Nilgiri Mountains.
- The Western Ghats lie to the south of the Nilgiris Mountains, to the south of the Nilgiris Mountains, the Western Ghats Mountains are known as the Annamalai Hills and the Cardamom Hills.
- The southernmost hill of the plateau of peninsular India is the Cardamom hill.
- Expansion of Nilgiri mountain is in three states –
- Tamil Nadu.
- Kerala
- Karnataka.

The plateau of Peninsular India consists of the following structures -
- Aravalli Mountains
- Malwa Plateau
- Vindhya Mountains
- Satpura Hill
- Chhota Nagpur plateau
- Western Ghat mountain
- Eastern Ghat Mountains
- Nilgiri Hills
- Deccan Plateau
- Annamalai Hill
- Cardamom hill
1. Aravali Mountains
- The extension of the Aravalli Mountains is at the north-western side of the plateau of peninsular India.
- The Aravalli mountain range extends from Palanpur in Gujarat to Majnu Teela of Delhi in north-east. Its length is about 800 Km.
- The maximum length of the Aravalli mountain range is in the state of
- The southern part of the Aravalli mountain is known as the Jarga hills.
- The Aravalli mountain near Delhi is known as Delhi Ridge.
- The highest peak of the Aravalli mountain is Guru Shikhar. It is located in Mount Abu (Rajasthan).
- The famous Jain pilgrimage centre Dilwarais located in Mount Abu.
- The Aravalli Mountain is the oldest fold mountain in the world.
- The Banas river crosses the Aravalli in the east to west direction and joins the Chambal river.
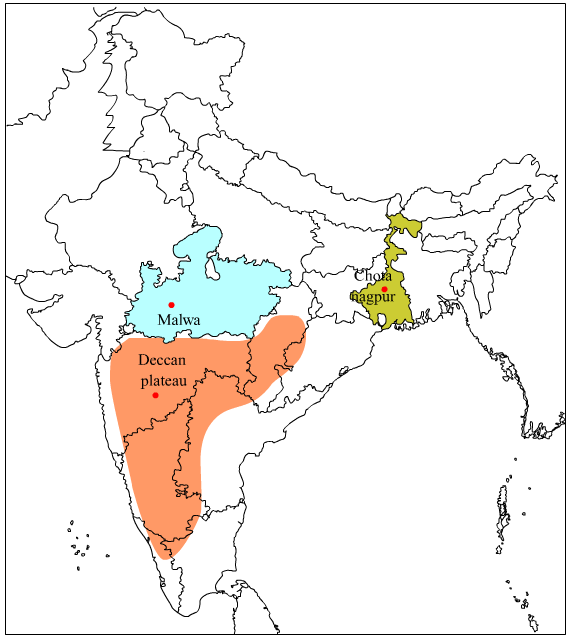
2. Malwa Plateau
- The plateau of Malwa lies to the south of the Aravalli range and the north of the Vindhya mountain, thus it can be said that the extension of the Malwa plateau lies between the Aravalli mountain and the Vindhya mountain.
- The slope of the Malwa plateau is towards the north that is why the Chambal, Betwa and Kali Sindh rivers flow in the north direction.
- The Malwa plateau is formed from lava emitted from the volcano, due to which black soil is found on the Malwa plateau.
- The Chambal River, Betwa River and Kali Sindh Riveroriginate from the Malwa Plateau.
- The Chambal and its tributaries have degraded the Malwa plateau, due to which the valley like figure is found here.
- The Chambal and its tributaries have degraded the Malwa plateau and converted it into Beehad khhadd, such erosion is called Gully erosion.
3. Chhota Nagpur Plateau
- Chhota Nagpur plateau is widespread in the state of Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- Two major rivers originate from the Chhota Nagpur plateau –
- Damodar River
- Golden Line River
- The Damodar river flows eastwards through the Chhota Nagpur Plateau in its rift valley and joins the Hooghly River in the state of West Bengal.

- Damodar river divides Chhota Nagpur plateau into two parts –
- Hazari Bagh plateau
- Ranchi Plateau
- Hazari Bagh plateau is situated to the north of Damodar river and Ranchi plateau is situated to the south of Damodar river.
- The Ranchi plateau is an example of the Flood plain in India.
Note - A plain of a plateau where rocky mounds or peaks are not found is called Flood plains.
- In India, three rivers flow in their rift valley –
- Narmada River
- Tapi / Tapti River
- Damodar River
- Ranchi, the capital of the state of Jharkhand is situated on the banks of the Subarnarekha River.
- Subarnarekha river flows towards the east and ends into the Bay of Bengal.
- Chhota Nagpur plateau is the richest plateau in India in terms of mineral wealth. Minerals like iron, coal, uranium are obtained from here.
- In India, uranium is obtained from Jadugoraunder Chhota Nagpur plateau.
- Chota Nagpur plateau is also called ‘Ruhr Region’ of India because it is rich in minerals
Note - Ruhr Region is in Germany. The area between Rur and Rhine rivers is called the Ruhr Region. It has rich reservoirs of minerals.
- To the north-east of the Chhota Nagpur plateau, are the Rajmahal hills. The Rajmahal hill is mainly located in the state of Karnataka.
4. Meghalaya Plateau or Shillong Plateau
- Shillong plateau is not an independent plateau but it is a part of the plateau of peninsular India. Although the location of the Shillong plateau is near the Himalayas it is, in fact, the eastern extension of the Rajmahal hill.
- Alluvial deposits -When rivers cut the mountainous area and fill sediments in the plains, it is called an alluvial deposit.

- The Shillong plateau consists of five hills –
- Garo
- Khasi
- Jaintia
- Mikir
- Rengma
- Garo, Khasi and Jaintia hills covered under Shillong plateau are located in the state of Meghalaya.
- Mikirand Rengma hills are located in the state of Assam under the Shillong plateau.
- The highest peak of the Shillong plateau is Nokrek located under the Garo hill.
5. Vindhya Range
- The Vindhya mountain range lies to the south of the Malwa plateau.
- Vindhya mountain range is spread in the state of Madhya Pradesh.

- Vindhya Mountain is known as Bhander hill and Kaimur hill in the east.
- Narmada Rift valley is located in the south of the Vindhya Mountain. The Satpura hill is situated to the south of the Narmada rift valley.
- Tapi Rift Valley is located in the south of Satpura hill.
6. Satpura Mountains
- The Satpura mountain is the only example of Block mountain in India.
- Narmada Rift valley is situated to the north of Satpura mountain and Tapi Rift valley is to the south of Satpura mountain.
Note - A mountain situated between two rift valleys is called Block Mountains.
- The Satpura mountain extends as three hills from west to east, their order from west to east is –
- Rajpipla Hill
- Mahadev Hill
- Maikal Hill
- Rajpipla is the westernmost hill of the Satpura Mountain.

- Mahadev hill is the middle hill situated on the Satpura mountain.
- Dhupgarh peak, the highest peak of Satpura mountain, is situated on the Mahadev hill.
- Amarkantak is the highest peak of Maikal hill.
- Maikal hill creates the border of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh
- Narmada and Son rivers originate near the Amarkantak peak. Narmada river flows into its rift towards the west and ends in the Gulf of Khambhat and Sone river flows towards north and merges in Ganga near Patna.
- Panchmarhi Hill Station/Panchmarhi Biosphere Reserve is located near Dhupgarh peak.
- The Satpura mountain range is spread in the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
7. Deccan Plateau
- The Deccan plateau is situated among the Satpura mountain range and the Western and Eastern Ghats.
- The Deccan plateau is mainly made up of rocks of the Deccan Trap.
- The following structures can be included under the Deccan Plateau –
- Harishchandra hill - Maharashtra
- Palghat Hill - Maharashtra
- Ajanta Hill - Maharashtra
- Gavilgarh Hill - Maharashtra
- Dandakaranya plateau is under Deccan Plateau.

- Dandakaranya plateau is mainly spread in the state of Chhattisgarh and
- Bastar plateau is located under the Dandakaranya plateau. It is situated to the south of the Dandakaranya plateau.
- Bastar plateau is the only tin storage in India.
8. Mahanadi Basin
- The Mahanadi Basin is situated to the north of the Dandakaranya plateau and in the middle of the Chhota Nagpur plateau in the state of Chhattisgarh.
- The area of Mahanadi Basin is very important for the production of paddy (Rice).
- In Uttar Pradesh, Chandaulidistrict is called ‘The Rice Bowl’.
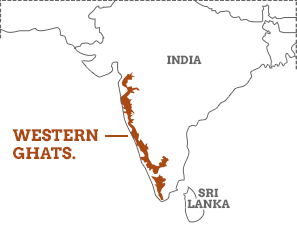
9. Western Ghat Mountains
- Starting from the mouth of the Tapi River, the Western Ghat Mountains extend till Capekemorinsouth to, Capekemorinitself is called Kanyakumari.
- The Western Ghat extends from north to south for about 1600 km.
- The Western Ghat Mountains are the second-longest mountain in India after the Himalayas.
- The Western Ghat Mountains are also called
- The Western Ghat Mountain is a Fault Scrap of the plateau of peninsular India rather than a mountain.
- The western fault scrap was formed as a result of the Indian plate breaking off from the African plate.
- Kalsubaiis the highest peak of Northern Sahyadri.
- Mahabaleshwar peak is to the south of Kalsubai peak on the western ghat.
- Mahabaleshwar peak and Kalsubai peak are located in the state of
- Three hills are located in the Saurashtra region under the state of Gujarat –
- Gir hill
- Barda Hill
- Mandava hill
- Asiatic lions are found in the Gir region of Gujarat.
- The Krishna River flows out of the Mahabaleshwar peak, towards the east and ends into the Bay of Bengal.
- There are mainly two peaks on the Western Ghats in the state of Karnataka -
- Kudremukh peak
- Brahmagiri peak
- Kaveri river originates from Brahmagiri peak in Karnataka state and flows in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu
- In South India, the Western Ghat Mountains and the Eastern Ghat Mountains combine to form a mountain knot, this mountain knot is called the Nilgiri Mountains.
- The highest peak of the Nilgiri Mountains is Dodabetta.
- The Nilgiri Mountains are in the states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala and
- Dodabettais the second highest peak in South India.
- Famous tourist destination Ooty is situated on Nilgiri hills in Tamil Nadu.
- The famous Evergreen Forest Silent Valley of Kerala is situated on the Nilgiri hills.
- Silent Valley is known for its biodiversity and dense forests.
- There is a mountain pass in the south of Nilgiri, it is called Palghat Pass.
- The state of Kerala and Tamil Nadu has been connected by road and rail via Palghat Pass.
- There is a mountain knot in the south of the Palghat Pass, which is called Anaimudi mountain knot.
- There are hills in three directions of the Anaimudi mountain knot –
- Annamalai towards the north
- Cardamom towards the south
- Palani hill towards the north-east
- The highest peak of Annamalai hill is Anaimudi.
- Cardamom hill is the southernmost hill of India.
- To the east of Anaimudi peak is the Palani hill, Palani hill is mainly located in the state of Tamil Nadu.
- The famous tourist destination Kodaikanal is located on the Palani Hills in the state of Tamil Nadu.
- The Palani hill is completely extended in the state of Tamil Nadu, while the Annamalai hill and the Cardamom hill lie on the border of Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- Passes are found at various places in the Western Ghat Mountains, these passes are helpful to cross the Western Ghat Mountains from the west to the east.
- Thalghat Pass is located on the Western Ghat in the state of Mumbai to Nagpur road passes through Thalghat Pass.
- The Bhorghat Pass is located on the Western Ghat in the state of The road from Mumbai to Pune passes through Bhorghat pass.
- National Highway No. 4 reaches Chennai via Mumbai and Pune, this highway also passes through the Bhorghat pass.
- Palghat Pass is situated in the state of Kerala in the middle of the Nilgiri and Annamalai Hills.
- The Shenkotta Pass is situated on the Cardamom hill. It is located in the state of
- The road from Thiruvananthapuram to Maduraipasses through the Shenkotta Pass.
10. Eastern Ghat Mountains
- The Eastern Ghat Mountain is not sorted and continuous like the Western Ghat Mountains, but rather than cut off from place to place.
- The slope of the peninsular Indian plateau is towards the east, due to which most of the rivers of peninsular India flow out of the Western Ghats and flow to the east coast. Like - Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri rivers.
- Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri rivers have cut the Eastern Ghat Mountains from place to place due to eastward flow.
- The Eastern Ghat Mountains between the delta of the Godavari and Krishna rivers have completely disappeared.
- The Eastern Ghat Mountains are known locally in different states. Like –
- Andhra Pradesh - Nallamalai, Palakonda and Velikonda
- Telangana – Seshachalam
- Tamil Nadu - Zawadi, Shevaraya, Panchamalaiand Sirumalai
- The hills of Tamil Nadu are made of charconite
- Sandalwood and teak trees are found in a large quantity in the hills of Tamil Nadu, including the Nilgiri Mountains.


Well explained...
ReplyDeleteGood
ReplyDeleteFound helpful