Previous Next
Indian Geography (Part-11)
Plains of India
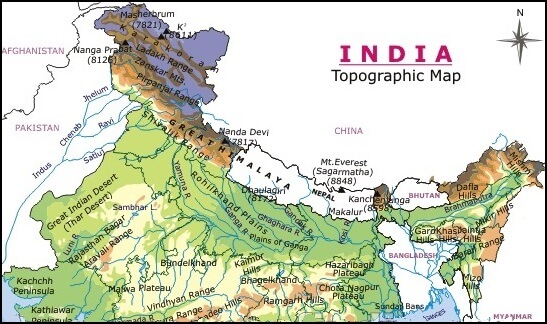
- The Indian plain can be divided into three parts for the study –
- Western Coastal Plain
- Eastern Coastal Plain
- Plain of North India
- The plateau of peninsular India divides the ridges into two parts for the convenience of study –
- Western Coastal Plains
- Eastern Coastal Plain
- Many rivers flow from the plateau of peninsular India into the Bay of Bengal and some rivers into the Arabian Sea. These rivers cut the plateau of peninsular India and deposit soil and sand towards the sea, due to this alluvial deposit, the western coastal plain and the eastern coastal plain have been formed.
- The western coastal plain is situated on the west side of the Western Ghats. The cities of Mumbai, Kochi, and Surat are located on the western coastal plain.
- The coastal plain to the east of the Eastern Ghats is called the Eastern Coastal Plain. Cities like Chennai, Visakhapatnam, and Bhubaneswar are located on the eastern coastal plain.
- The eastern coastal plains and the western coastal plains have been formed by rivers originating from peninsular India.
- Western coastal plain
- The western coastal plain extends from the state of Gujarat to Kanyakumari.
- Kanyakumari is also known as Capekemorin.
- The maximum width of the western coastal plain is at the mouth of rivers Narmada and Tapi.
- The area from Gujarat to Goa is called Konkan coast.
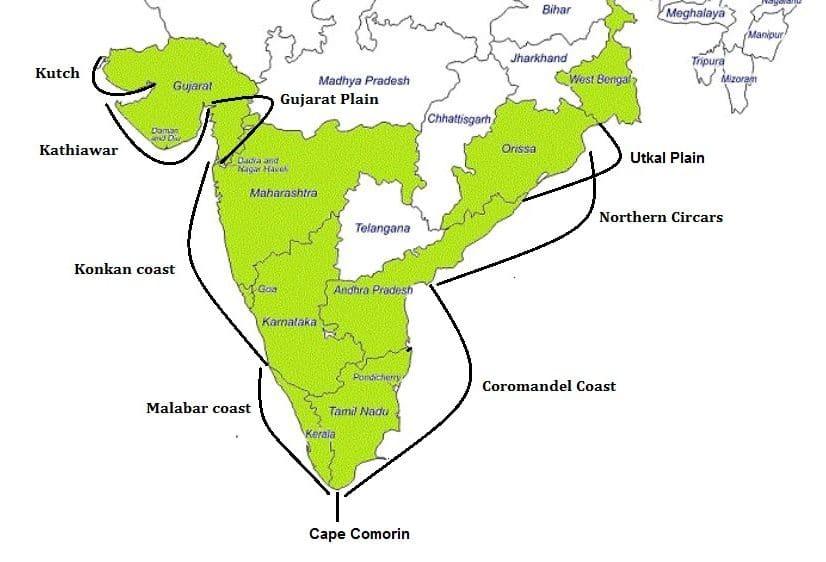
- From Goa to Mangalore of Karnataka, it is called Kannada coast and from Mangalore to Kanyakumari, it is called Malabar Coast.
- Most of the Malabar Coast is in the state of Kerala.
- The seawater situated on the ground that is surrounded by land from all sides is called Lagoon Lake so Lagoon Lake is a saltwater lake.
- Some lagoon lakes are found on Malabar coast, for example- Kerala’s Vembanad lake and Ashtamudi Lake.
- Lagoon lakes are locally called Kayal in Kerala.
- The western edge of the Western Ghats is corner like, i.e. its slope is very sharp. Due to the steep slope, the rivers flowing on the Western Ghats, which flows towards the west, are very fast. These rivers build estuaries on their mouth.
- The Narmada and Tapti rivers in Gujarat and the Sharavati in Karnataka and the Mandvi, Zuari rivers in Goa form estuaries. Similarly, in Kerala, the Bharatpuja and Periyar rivers form estuaries.
- Panaji, the capital of Goa, is situated on the banks of the Mandvi River.
- East Coast Plains
- The eastern coastal plains are formed by the delta region of rivers, in other words, the alluvial deposits of rivers have formed the plains of the east coast.
- In the alluvial deposit, the rivers bring fertile soil every year, which is why the Eastern Ghats Plain is very fertile.
- Especially the eastern coastal plain region is suitable for paddy (rice) cultivation.
- Paddy is cultivated in sufficient quantity in the valleys of Cauvery and other rivers on the Coro Mandal Coast.

- The extension of the eastern coastal plain is from the mouth of the Hooghly River to Kanyakumari.
- Tamil Nadu state has the highest width of the eastern coastal plain.
- The eastern coastal plain in Orissa is called Utkal Beach.
- The Godavari and Krishna rivers form their deltas in Andhra Pradesh.
- Western Ghats rivers build estuaries on their mouths while Eastern Ghats rivers build delta on their mouths.
- The land between the Utkal coast in Odisha and the Godavari and Krishna rivers in Andhra Pradesh is called the Northern Circars.
- Pulicat lake is a lake situated on the border of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, although Pulicat lake is located in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- The coastal plain of Tamil Nadu is called the Coro Mandal coast.
- There are also some Lagoon lakes on the eastern coastal plain, like Chilika Lake in Orissa and Pulicat Lake in Andhra Pradesh.
- Sri Hari Kota Island is situated in the heart of Pulicat Lake.
- Satish Dhawan Space Center is located on Sriharikota Island located in Pulicat Lake.
- Plains of north India
- The Himalayan Rivers carry very large rocks with them. Due to the steep slope of the mountains in the mountainous areas, these rivers bring along the rocks, but due to the low slope in the Shivalik region, they deposit these rocks in the Giripad area of Shivalik. This area is called Bhabar Pradesh.
- The lower area of the mountain is called Giripad.
- In terms of terrain, the plain area of North India has been divided into -

A. Bhabar Pradesh
B. Terai Pradesh
C. Khadar Pradesh
D. Bangar Pradesh
A. Bhabar Pradesh
• Bhabar Pradesh spans in the south of the Lesser Himalayas from Sindhu river to Teesta river parallel to Shivalik Himalayas.
• When the rivers originating from the Himalayas reach the Bhabar region, they enter large rocks, due to which the rivers become extinct on the surface.
• The Bhabar region is not arable due to the rock block, that is why arable land is not available here.
• Bhabar Pradesh extends from west to east direction from Indus river to Teesta river in Giripad region of Shivalik.
B. Terai Region
• When the rivers come out of the Bhabar region, the water of the rivers gets dispersed due to the rocks. That is why there is no clear stream of rivers in this area.
• The water of the rivers is so dispersed from Bhabar region that marshy areas are formed in the south of Bhabar region from the Indus to the Teesta River. In these marshy areas, many creeping creatures and poisonous pests are found. After the Bhabar region, the marshy area is called the Terai region or plain.
• The Terai region is the best area for paddy cultivation.
C. Khadar Pradesh
• Khadar regions are formed due to alluvial deposits brought by the rivers in the plains of North India. Since sediments are deposited by rivers every year, due to which these regions are very fertile.
D. Bangar Pradesh
• In the regions of North India, the regions located away from the rivers where the floodwater of the rivers cannot reach due to the height, such regions are called Bangar Pradesh.
• Bangar Pradesh is an area of the old alluvial regions. It is relatively less fertile.

No comments:
Post a Comment